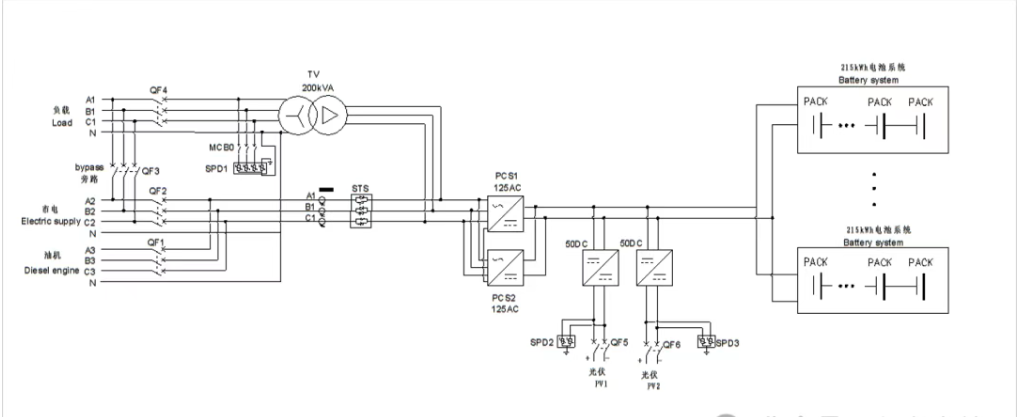
PCS Energy Storage Converter Explanation
Here is the detailed explanation of the PCS (Power Control System) energy storage converter to help you understand and learn about this device. The PCS is a critical component in energy storage systems, primarily responsible for the conversion and control of electrical energy, enabling bidirectional power flow among the grid, the energy storage system, and the load.
Basic Concept and Functions of PCS
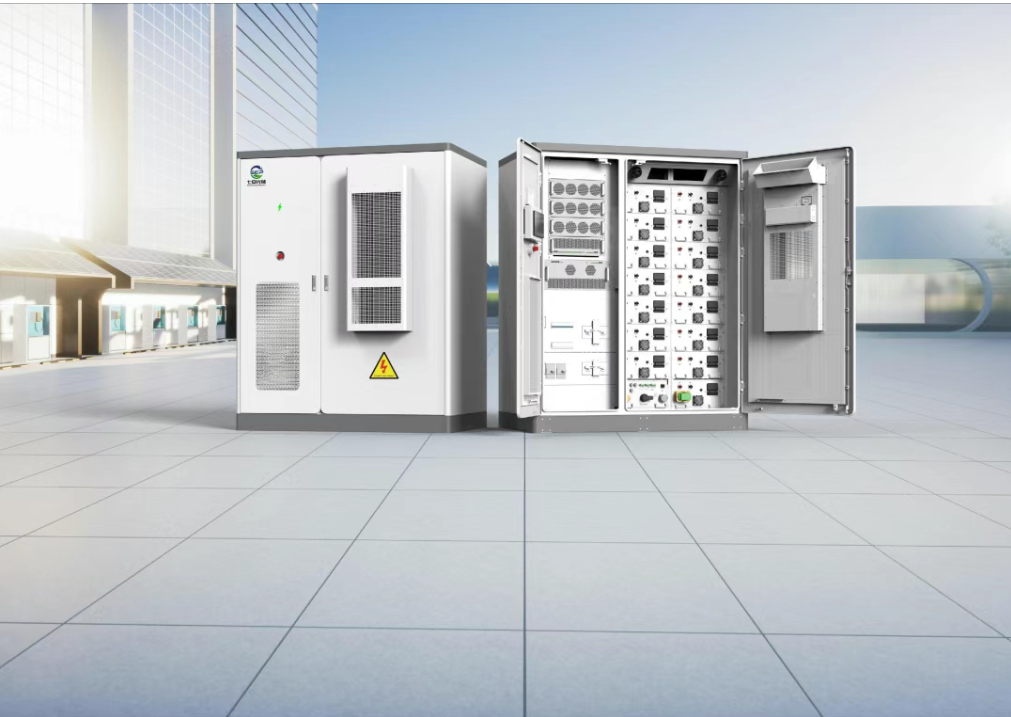
The PCS is mainly responsible for converting between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), which is a fundamental function in the interaction between energy storage systems and the grid. It not only facilitates energy conversion but also ensures stable system operation through precise control. The PCS is equipped with functions such as energy management and equipment protection, making it a core component of energy storage systems.
Working Principle of PCS
The PCS utilizes power electronic conversion technology, employing high-frequency switching to control power devices (such as IGBTs), enabling flexible operation across all four power quadrants. This allows the PCS to dynamically adjust the ratio of active and reactive power according to grid demands, supporting reactive power compensation and voltage regulation in the grid.
Technical Parameters and Classification of PCS
Technical parameters include input/output voltage range, efficiency, power loss, etc. Depending on the application scenario, PCS can be classified into residential, commercial & industrial, and large-scale energy storage power station types, each differing in power rating and functionality.
Development Trends and Challenges of PCS
With advancements in power electronics technology, the conversion efficiency of PCS continues to improve, while its size and weight gradually decrease, and costs decline. Future trends in PCS development include higher efficiency, intelligence, and modular integration, enabling its application in a broader range of scenarios.
Application Scenarios of PCS
PCS is widely used in renewable energy grid integration, smart microgrids, industrial and power systems, smart homes, and other fields. For example, in photovoltaic power generation systems, PCS can convert DC power into AC power and feed it into the grid. In demand response markets, PCS can rapidly adjust output power in response to grid commands.
This information should help you understand and demonstrate the key features and applications of PCS energy storage converters. In the next issue, we will introduce you to energy storage BMS (battery management system)