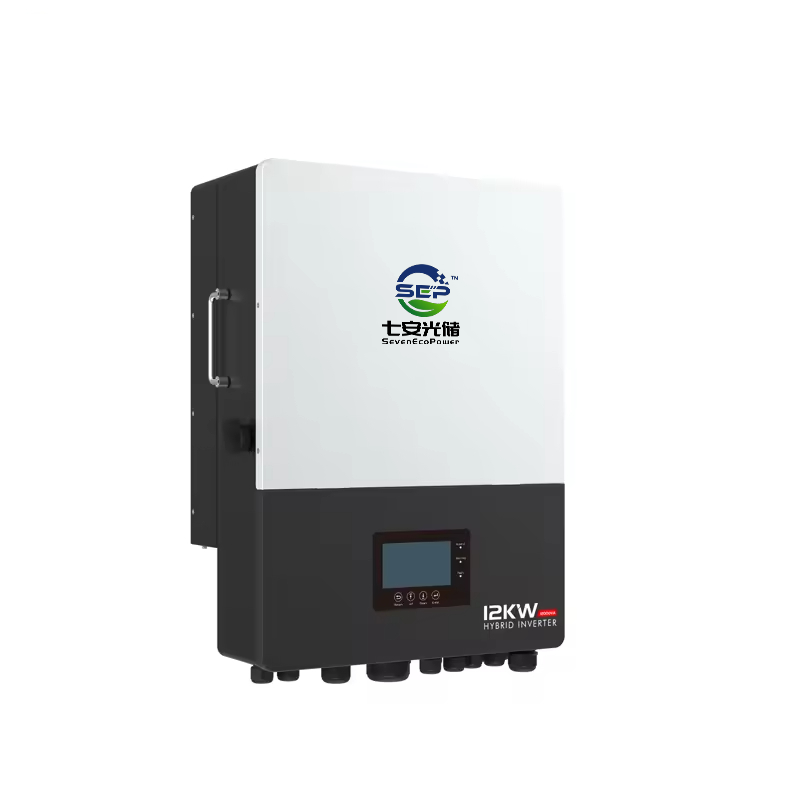
12kW 3-Phase Hybrid Inverter solar battery
Product Features
1. 12kW EPS Output
2. 10 units Paralleling
3. AC Couple to retrofit existing solar system
4. Support Wi-Fi for mobile monitoring
5. 3 MPPT Input for max input 18kW
6. Separated Generator Input
7. 200A AC Passthrough Current
8. PV Module Monitoring
9. Peak Shaving Function
10. Color LCD, Touch Scree
11. Maximum PV Self-Consumption
12. Peak Load Shifting
13. UPS Level
14. Peak Valley Mode
15. Off-grid
16. 0-injection
The 12kW 3-Phase Hybrid Inverter with Solar Battery is the core equipment of medium and large-scale solar systems, which is mainly used to connect photovoltaic arrays, power grids, energy storage batteries and loads to achieve efficient conversion, distribution and storage of electric energy. Its design takes into account the three functions of grid-connected power supply, energy storage management and off-grid backup, and is the core hub of "flexible energy dispatch" in modern solar energy systems. Here's a closer look at it in solar equipment:
Core functions and how it works
In a solar energy system, the core functions of the device are achieved through the following processes:
Photovoltaic power conversion and preferential self-consumption
The direct current (DC) generated by the photovoltaic panels is connected to the inverter, which efficiently converts the DC power into three-phase alternating current (AC) through MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) technology, giving priority to local three-phase loads (such as factory equipment, commercial air conditioners, etc.), reducing dependence on the grid.
Energy storage and grid-connected distribution of excess electric energy
When the photovoltaic power generation > the load power consumption, the excess electric energy is preferentially charged to the supporting solar cells (through the charge and discharge management module of the inverter, the battery is controlled to charge at the best current to prolong the life); If the battery is fully charged, the remaining power can be integrated into the grid (subject to local grid connection standards) to achieve "electricity sales income".
Grid interaction and peak-to-valley arbitrage
When the photovoltaic power generation < the load electricity consumption, the inverter automatically replenishes the difference from the grid to ensure the stable operation of the load;
If equipped with an intelligent algorithm, the battery can be charged by taking electricity from the grid during the "low price period" of the grid, and discharging the battery to supply the load during the "peak price period", reducing the electricity bill (i.e., "peak-to-valley arbitrage").
Off-grid backup and emergency power supply
When the power grid is cut off: the inverter immediately switches to "off-grid mode" (usually < 10ms, non-perceptual switching), and the solar cells and photovoltaic panels jointly supply power to the load (when the photovoltaic power supply is insufficient, the battery replenishes energy) to ensure that the operation of key equipment (such as servers and medical equipment) is not interrupted.